Questions and answers on conscious guidance and coordination
Understanding the principles, practice and mechanics of postural re-education.
When learning conscious movement, certain questions arise repeatedly.
- How does conscious guidance work?
- Why is feeling an unreliable guide?
- How does rational control differ from traditional posture training?
This section provides clear, practical answers to the most common questions about postural re-education. The explanations are based on the principles of F. M. Alexander and integrate theoretical understanding with practical experience. They will help you understand the mechanisms of conscious coordination and apply the process of change with clarity and purpose.
In what ways does this approach differ from physiotherapy or fitness training?
Traditional methods tend to focus on the end result, such as reducing pain or strengthening muscles. However, this approach does not address the underlying cause, meaning the pain inevitably returns. Symptoms are treated in isolation, while the underlying coordination patterns often remain unchanged. In contrast, the conscious guidance method shifts the focus to the means by which movement is initiated and organised. By reorganising the entire coordination and posture system, this approach leads to greater efficiency, improved balance and long-term structural stability.
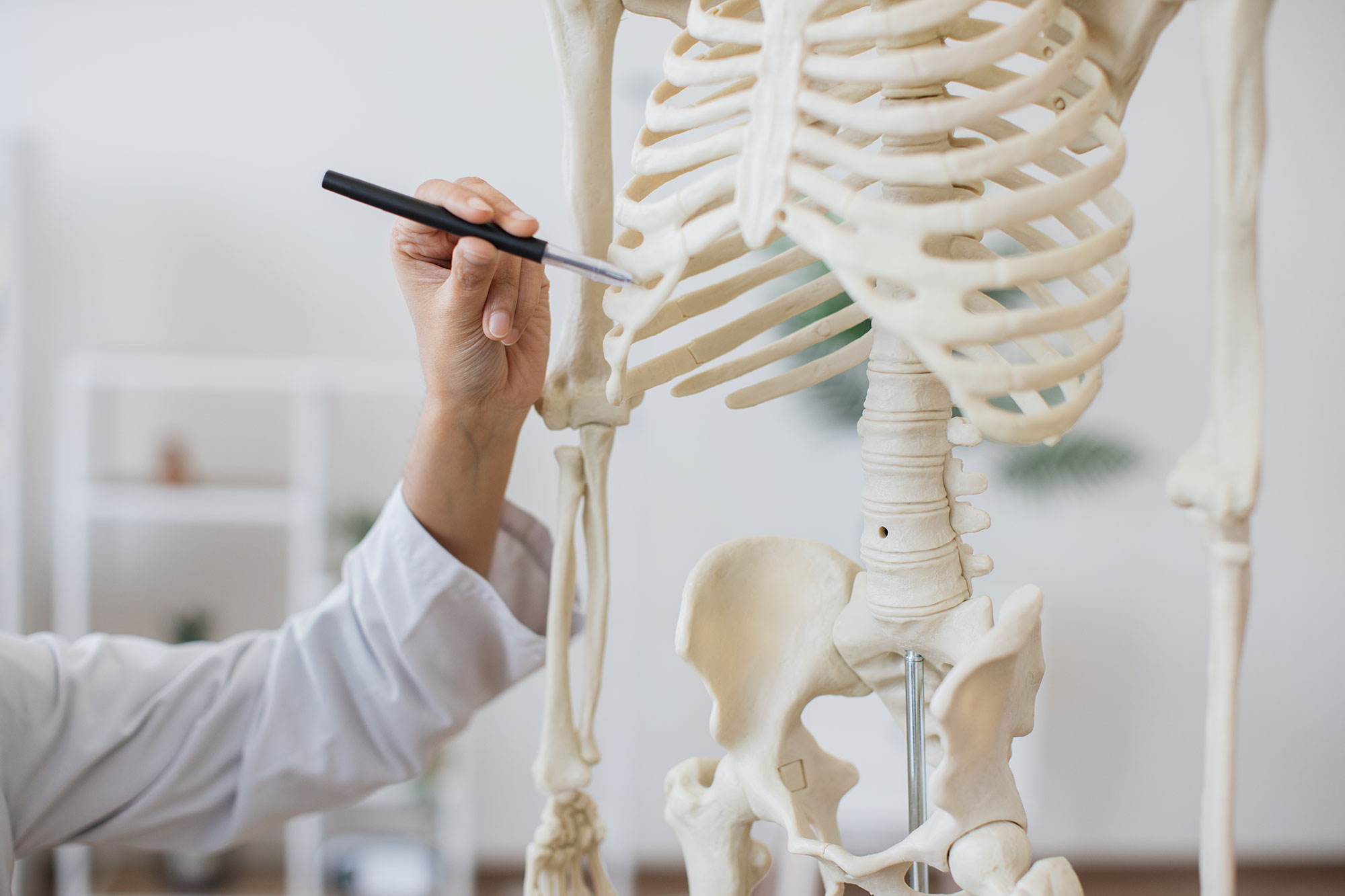
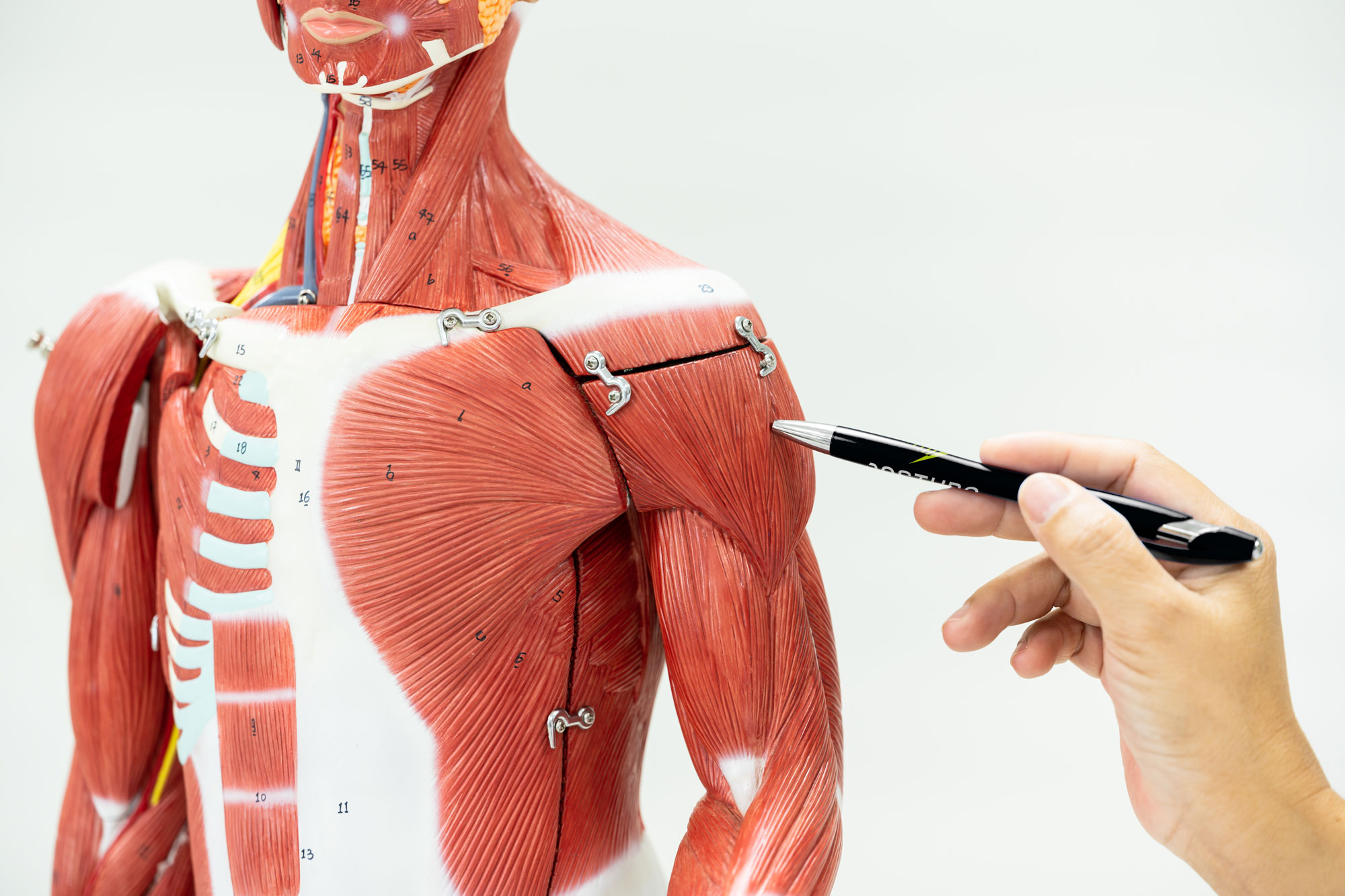
Why is the torso the key, and what does primary control mean?
The torso mechanism lies at the heart of bodily organisation, influencing posture, balance and movement coordination.
F. M. Alexander referred to the conscious orientation of this mechanism as 'primary control'. It governs the dynamic relationship between the head, neck, and back. When the torso is shortened or misdirected, tension and faulty movements arise. However, expanding and lengthening the torso mechanism decompresses the spine, enabling the whole body to operate freely, efficiently, and in coordinated unity.
What role do fascia and elastic tension play in stability?
Fascia forms a continuous elastic network that connects muscles and other structures throughout the body. The tension in this network does not arise from muscular effort, but from antagonistic actions – opposing movements that naturally and integrally lengthen the tissue. This elastic tensile force stabilises the body without requiring excessive muscular effort.
However, when the fascia lose tone, the body collapses, structural support is reduced, and the musculature is forced to compensate.
Why does correct movement often feel wrong at first?
Habitual misdirection becomes embedded in the nervous system and therefore feels 'right'.
When movement is executed consciously and under reasoned control, however, it contradicts the familiar sensory pattern and therefore feels strange or awkward.
This method teaches you to disregard this unreliable sensory perception and follow conscious, reasoned instructions instead. Only then can the nervous system accept the new, correct coordination as natural.
How can verbal instructions be used to alter physical structures?
Verbal instructions are precise tools used by the reasoning mind to direct movement.
Rather than acting instinctively, a sequence of reasoned thoughts is formulated to organise the body indirectly. This conscious projection replaces unreliable instinct with clear mental guidance.
The body then follows this logical plan, enabling new, coordinated movements to emerge and producing lasting postural change.
How can success be defined and measured objectively?
Success cannot be determined by subjective comfort, since sensory appreciation is unreliable. Instead, it is defined by the objective attainment of mechanical balance, which is expressed through a stable tendency to lengthen the torso during movement.
Progress becomes visible through conscious control, visual analysis and external feedback.
Only by observing what is actually happening in the body can self-correction be achieved and real change be confirmed, regardless of how it feels.
What effect does this method have on internal functions, pain and performance?
- Breathing and internal functions:
Freeing the thoracic mechanism and lengthening the spine allows the diaphragm to regain mobility. This improves respiration, circulation and digestion, enabling the body's systems to function more efficiently.
- Chronic pain:
Correct alignment distributes load evenly and eliminates unnecessary muscular tension.
- Performance:
A stable, expansive structure conserves energy and enhances coordination, efficiency, and power during any activity.
How can this method achieve lasting change when other approaches have failed?
Other methods often fail because they rely on subconscious guidance, which cannot organise complex coordination reliably.
This approach shifts control to the reasoning mind. By consciously inhibiting faulty impulses and applying the means-whereby principle, movement can be reorganised step by step.
The result is a sustainable re-patterning of general coordination that is stable, precise and long-lasting.
Which approach is used primarily: the Alexander approach or the Masoero approach?
This system combines the core principles of conscious guidance and control from the Alexander approach with the analytical model of the Masoero approach.
Movements are defined geometrically and directed via precise verbal instructions to achieve quantifiable improvements in coordination.
Thus, the method combines Alexander's philosophy with a systematic, rational approach that goes beyond purely somatic methods.
Who is this method suitable for?
It is suitable for people of all ages and fitness levels who wish to improve their movement and balance. It is particularly beneficial for those with sedentary jobs, chronic pain or limited mobility, as well as for athletes looking to improve their coordination and prevent injury.
The programme identifies and replaces unconscious movement habits – patterns shaped by daily life, imitation and environmental demands – with efficient, natural coordination.
I am over 50. Is it still possible to improve my alignment?
Yes, absolutely. The nervous system can learn and develop new coordination patterns at any age. Even after decades of ingrained habits, it is possible to effect meaningful change when movement is guided by conscious, reasoned instruction rather than feeling. This method teaches you to inhibit old habits and gradually reorganise your body to become more upright and coordinated.
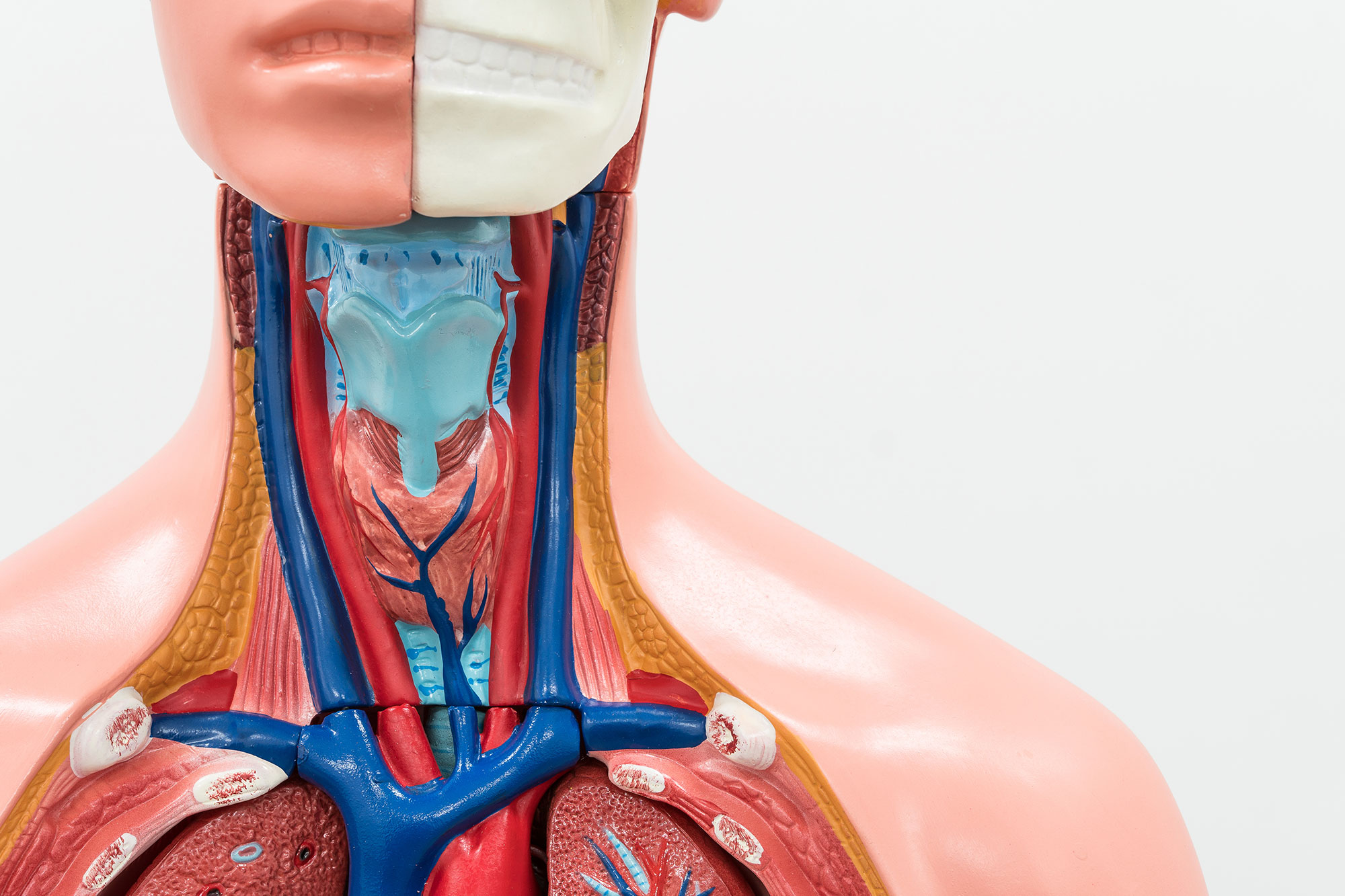
How does this method positively affect internal functions, such as breathing?
The function of the internal organs depends on the length and mobility of the torso.
Decompressing the spine and consciously opening the rib cage enables the diaphragm to move freely once more. This improves breathing, circulation and digestion, as the organs regain adequate space and support.
What if my pain comes and goes?
Fluctuating pain indicates general instability in coordination and signals that the body is intermittently reverting to old patterns.
Through conscious awareness, you can learn to identify movements that trigger discomfort and gradually reorganise them. This replaces shortening habits with integrated coordination, resolving the underlying cause of the pain sustainably.
What should I do if I cannot attend the live sessions?
If fixed appointments are difficult, daily video feedback is a more flexible option.
You send us short clips of your movements and receive professional feedback via chat or video. This allows you to make regular corrections, track your progress and fit the training into your daily routine.
This format allows for continuous development and growing independence, eliminating the need for scheduled live sessions.
What is the significance of torso lengthening and fascial tension?
Torso lengthening involves bony segments moving in opposite directions in a precise geometric relationship. This stretches the connective tissue, creating an elastic counter-tension known as 'antagonistic pull'.
This passive, non-muscular support system stabilises the body, enabling efficient, integrated, sustainable movement with minimal effort.







 Instagram
Instagram Facebook
Facebook TikTok
TikTok YouTube
YouTube